A volcano is an opening in the Earth's surface through which molten rock, ash, and gas escape. Volcanoes are formed by the movement of tectonic plates in the Earth's mantle. When two plates diverge or converge, magma can be produced and eventually pushed to the surface through a vent, creating a volcano. There are different types of volcanoes, including shield, cinder cone, and stratovolcanoes, each with distinct characteristics and shapes.
Volcanic activity can range from relatively mild eruptions that release ash and gas to more explosive events that can discharge massive amounts of ash and lava. Volcanic eruptions can cause widespread damage to life and property, including the release of dangerous gases, such as sulfur dioxide, and the production of ash and volcanic rock that can trigger landslides, flash floods, and other hazards.
Volcanoes can also have positive effects, such as creating new land masses, enriching soil with nutrients, and producing geothermal energy. Despite the dangers they pose, many people are drawn to the unique beauty and geological significance of volcanic landscapes, and they continue to be popular tourist destinations. In order to better understand the behavior of volcanoes and mitigate their impacts, volcanologists study the formation, structure, and activity of these geological wonders.
Why it is Called Volcano?
The term "volcano" originates from the Roman name for the island of Vulcano, one of the Aeolian Islands located off the coast of Sicily, Italy. The island was named after the Roman god of fire, Vulcan, and was known for its frequent volcanic eruptions and the presence of steam vents and hot springs.
In the ancient world, volcanoes were often seen as places of myth and legend, associated with powerful forces of nature and the gods themselves. This view persisted into the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, when many famous European explorers and naturalists studied and wrote about the volcanoes of Italy and other parts of the world.
As our understanding of geology and the Earth's structure grew, the term "volcano" became more widely used to describe similar geological features found around the world. Today, the word is used to describe any mountain or hill formed by the accumulation of solidified lava and other volcanic material, and it has become a widely recognized and accepted term in the scientific and popular vocabulary.
In summary, the term "volcano" is derived from the name of the Roman god of fire, Vulcan, and the island of Vulcano, and it has come to represent the powerful and awe-inspiring geological features created by volcanic activity.
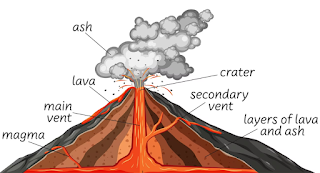
Volcano With Diagram?
A volcano consists of three main parts: the vent, the magma chamber, and the slopes or cone. The vent is the opening through which magma, ash, and gases escape to the surface. The magma chamber is the underground reservoir where the magma is stored before it reaches the surface. The slopes or cone, also known as the volcanic edifice, is the steep-sided pile of volcanic ash, cinders, and lava flows that forms the characteristic shape of a volcano.
Volcanoes are categorized based on the type of material they erupt and the shape of their slopes. There are four main types of volcanoes: shield, cinder cone, composite, and lava dome. Shield volcanoes are broad and gently sloping, and they are made of low-viscosity lava that flows easily and covers a large area. Cinder cone volcanoes are steep and cone-shaped, and they are formed from explosive eruptions that release ash and cinders. Composite or stratovolcanoes are steep and symmetrical, and they are made of alternating layers of ash, cinders, and lava flows. Lava dome volcanoes are steep-sided mounds of solidified lava that form during explosive eruptions.
These are the basic parts and types of a volcano, but there is much more to learn about these fascinating geological features.
Types of Volcanoes?
There are four main types of volcanoes:
Shield Volcanoes: They are broad, gently sloping mountains composed of fluid lava flows. Shield volcanoes are formed from the buildup of many thin lava flows, and they are usually found in areas where the tectonic plate is spreading apart.
Cinder Cone Volcanoes: They are steep, conical mountains formed by explosive eruptions that eject ash, cinders, and rocks. Cinder cone volcanoes are relatively small and have a circular shape.
Composite Volcanoes (Stratovolcanoes): They are large, steep-sided cones composed of multiple layers of ash, cinders, lava flows, and volcanic rock. Composite volcanoes are formed by alternating explosive and effusive eruptions, and they are often found along subduction zones where one tectonic plate is sliding under another.
Lava Domes: They are steep-sided mounds of solidified lava that form during explosive eruptions. Lava domes can be found within the craters of larger composite volcanoes or as standalone features.
Each type of volcano has distinct characteristics, such as shape, size, eruption style, and type of material erupted. It is important to understand the different types of volcanoes in order to predict their behavior and potential hazards.
Volcano Eruption and USA
Volcanic eruptions have occurred throughout the history of the United States, with many active and potentially active volcanoes located throughout the country, particularly in Alaska and Hawaii. Some of the most notable volcanic eruptions in the United States include:
Mount St. Helens, Washington: On May 18, 1980, Mount St. Helens experienced a catastrophic eruption that caused widespread destruction and 57 deaths. The eruption was one of the most destructive in U.S. history and remains one of the most well-studied volcanoes in the world.
Kilauea, Hawaii: Kilauea is one of the most active volcanoes in the world and has been erupting continuously since 1983. The volcano is located within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park and has caused widespread damage and destruction, including the destruction of entire towns.
Mount Rainier, Washington: Mount Rainier is a potentially active stratovolcano located near Seattle, Washington. The volcano has a history of small-to-moderate eruptions and is considered one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the United States due to its proximity to populated areas.
Mount Lassen, California: Mount Lassen is a composite volcano located in northern California that last erupted in 1915. The eruption was one of the last in a series of volcanic eruptions in the area and caused widespread ash fall and mudflows.
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) closely monitors volcanic activity in the United States and provides information and warnings to the public in case of an impending eruption. In order to mitigate the impacts of volcanic eruptions, it is important to understand the behavior of these geological features and to be prepared for potential hazards.
What are Volcanoes Class 7?
Volcanoes are geological features that form when molten rock (magma) and ash escape from the Earth's interior and reach the surface. They are considered a type of natural hazard, as they can cause significant damage to surrounding areas and release dangerous gases into the atmosphere.
Here are some key concepts related to volcanoes for a Class 7 student:
Formation: Volcanoes form when magma rises to the surface through a vent or opening, and erupts in a fiery explosion. This creates a cone-shaped mountain that gradually builds up over time.
Types of Volcanoes: There are four main types of volcanoes: shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava dome volcanoes. Each type has distinct characteristics, such as shape, size, eruption style, and type of material erupted.
Volcanic Eruptions: Volcanic eruptions can be explosive or effusive. Explosive eruptions are characterized by ash clouds and ash falls, while effusive eruptions produce fluid lava flows.
Hazards: Volcanic eruptions can cause a number of hazards, including ash fall, mudflows, lahars, and release of toxic gases. They can also trigger earthquakes, and cause damage to buildings, infrastructure, and crops.
Monitoring: Scientists monitor volcanic activity in order to predict and prepare for potential eruptions. They use various tools and techniques, such as seismographs, gas sensors, and satellites, to track changes in the volcano's behavior.
These are some of the basic concepts related to volcanoes that a Class 7 student should know. Understanding the nature and behavior of these geological features can help us prepare for and mitigate the impacts of volcanic eruptions.
15 volcano Names
Here is a list of some of the most well-known volcanoes around the world:
- Mount Vesuvius, Italy
- Mount St. Helens, United States
- Kilauea, Hawaii, United States
- Mount Etna, Italy
- Mount Rainier, United States
- Mount Fuji, Japan
- Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania
- Mount Popocatépetl, Mexico
- Eyjafjallajökull, Iceland
- Mauna Loa, Hawaii, United States
- Mount Pinatubo, Philippines
- Galeras, Colombia
- Mount Merapi, Indonesia
- Villarrica, Chile
- Pacaya, Guatemala
This is by no means an exhaustive list, as there are many other active and potentially active volcanoes located around the world. Some of the largest and most explosive volcanoes are located along the Pacific "Ring of Fire," a region of tectonic activity that is prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Volcano Facts
Here are some interesting facts about volcanoes:
Volcanoes can form anywhere on the Earth's surface, but most are located along the boundaries of tectonic plates.
Volcanoes are formed when magma rises to the surface and solidifies, building up over time to form a cone-shaped mountain.
Some of the largest and most explosive volcanoes are located along the Pacific "Ring of Fire," a region of tectonic activity that is prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Volcanic eruptions can release huge amounts of ash and gas into the atmosphere, affecting air quality and weather patterns for months or even years after the eruption.
The largest volcano in the solar system is Olympus Mons on Mars, which is nearly three times taller than Mount Everest.
The eruption of a super-volcano, such as Yellowstone Caldera in the United States, could have global consequences, including ash fall and toxic gas releases that would impact the entire planet.
Volcanic eruptions can also create new land, as seen in Hawaii where new islands have formed over time from repeated eruptions.
Some of the most active and well-known volcanoes in the world include Mount Vesuvius in Italy, Kilauea in Hawaii, and Mount St. Helens in the United States.
Scientists use various tools and techniques, such as seismographs, gas sensors, and satellites, to monitor volcanic activity and predict potential eruptions.
Despite their destructive power, volcanoes are also important for the Earth's ecosystem, as they release minerals and nutrients into the soil that support plant and animal life.
These are just a few of the interesting facts about volcanoes. Understanding these geological features and their behavior is important for predicting and mitigating the impacts of volcanic eruptions.


Post A Comment:
0 comments so far,add yours